You Must Know
1. Materials can be either pure substances, or a mixture of two or more substances.
2. A pure substance has only one kind of particles in it.
3. Mixtures consists of two, or more, substances.
4. Mixtures are classified as homogeneous and heterogeneous.
5. Mixtures can be divided into three categories-
(i) solids with solids
(ii) solids with liquids
(iii) liquids with liquids.
6. Methods of separating solid-solid mixtures are-
hand picking threshing
winnowing sieving
magnetic separation sublimation
7. Solid-liquid mixtures are of two types-
(i) solids that dissolve in liquids. Such mixtures can be separated using evaporation and crystallisation.
(ii) solids that do not dissolve in liquids. Such mixtures can be separated out by the process of sedimentation and decantation, filtration or centrifugation.
8. A mixture, of two immiscible liquids, can be separated using a separating funnel.
Something To Know
A. Fill in the blanks.
1. Housewives sometimes use the method of handpicking to remove unwanted substances from eatables like rice and pulses.
2. Common salt is prepared on a large scale through the process of evaporation/crystalisation.
3. Separation of tea leaves from tea is done by a process called filtration
4. The process of loading can be used to increase the rate of sedimentation of the suspended particles in a solid-liquid mixture.
5. The method, used to separate the fine particles, suspended in a liquid, by rotating the mixture at high speed, is known as centrifugation.
B. Match the following:
1. Wind (b) winnowing
2. Chalk powder and water (c) sedimentation
3. Oil and water (e) separating funnel
4. Separating peas from cooked pulao (a) hand picking
5. Muslin cloth (d) filtration
6. Camphor and salt (f) sublimation
C. Tick (✔) the correct option.
1. Which of the following is an example of a heterogeneous mixture?
sugar in water
an aerated drink
pebbles in rice (✔)
salt in water
Answer – pebbles in rice(✔)
2. Which one of the following is not an example of a not an example of a pure substance?
oxygen
copper
air (✔)
carbon dioxide
Answer – air(✔)
3. The process of loading helps to-
slow down the rate of sedimentation
speed up the rate of sedimentation (✔)
speed up the rate of decantation
slow down the rate of decantation
Answer – speed up the rate of sedimentation(✔)
4. Transferring the clear liquid, into another container, leaving behind the residue, is called-
sedimentation
condensation
decantation (✔)
crystallisation
Answer – decantation(✔)
5. A substance, that sublimes easily, is-
naphthalene (✔)
sugar
salt
chalk
Answer – naphthalene(✔)
D. Answer the following questions in brief.
1. Name any three methods used for separating a solid-solid mixture.
Answer – Hand-picking, winnowing, sieving
2. What is winnowing? Give an example of a mixture whose components can be separated by this method.
Answer – Winnowing is the method to separate the lighter husk from heavier grains like wheat. In this method, the mixture is allowed to fall from a height.
Example- The lighter components (the husk) get blown away to a distance while the heavier components, or the grains, fall closer. The two parts get separated into two separate heaps.
3. Some iron pins get scattered on the carpet when you are expecting guests. How can one collect all the pins in the shortest possible time?
Answer – Iron nails can be collected in the shortest possible time by bringing a magnet near them. The iron nails will cling to the magnet.
4. Name any three substances which sublime on heating.
Answer – Three substances that sublime on heating are naphthalene, camphor, and iodine.
5. What is crystallisation? Name any three substances which can be purified using this technique.
Answer – Crystallization is a process that separates a pure solid, in the form of its crystals, from a saturated solution. The three substances which can be purified using this technique are salt, crystals of alum, and blue vitriol.
E. Answer the following questions.
1. Differentiate between a pure substance and a mixture. Give two examples of each.
Answer – A pure substance is made up of only one type of substance whereas a mixture is formed when two or more substances are mixed in any proportion.
Examples of pure substances are sugar, oxygen. Examples of the mixture are air, seawater.
2. State the difference between heterogeneous and homogeneous mixtures. Give two examples of each type.
Answer – Homogeneous mixture is that which has the same composition throughout, that is, its components are uniformly distributed. Examples are solutions of salt and water, and soft drinks.
Whereas a heterogeneous mixture is that which does not have the same composition, throughout, that is its components are not uniformly distributed. Examples are a mixture of sand in water, pebbles in rice.
3. Can a mixture of iodine and camphor be separated by the sublimation method? Give reason for your answer.
Answer – No, the mixture of iodine and camphor cannot be separated by sublimation method because both iodine and camphor sublime on heating that means they directly change into the gaseous state without changing into liquid on heating.
4. Why does the size of naphthalene balls, put in open, keep on reducing with time?
Answer – The size of naphthalene balls put in open keeps on reducing with time because naphthalene sublimes on heating and when it is kept open, it absorbs the heat from the atmosphere and the surface on which it is kept and sublimes slowly.
5. After a dust storm, how does rain help in making air clear?
Answer – Dust particles in the air get loaded with rainwater and settle down. This, the loading helps in clearing the air after a dust storm.
6. Sawdust, mixed in water, cannot be separated by the sedimentation method. Why?
Answer – The sawdust mixed in water cannot be separated by the sedimentation method because the particles of sawdust are small and very light, so they are suspended in water and don’t settle down on the bottom of the container.
7. The filtration method cannot be used to separate sugar and salt mixed in water. Why?
Answer – Sugar and salt are soluble in water and the filtration method is used to separate insoluble solid impurities from water.
8. Describe the method of centrifugation using an appropriate example.
Answer – Centrifugation is a method used to separate the fine particles suspended in a liquid by rotating the mixture at high speeds.
Example- Separating cream from milk by churning it. The heavier particles that are the buttermilk tend to settle down at the bottom of the container when the lighter cream containing the butter stays at the top.
Value Based Question
The students, of Class-VI, participated actively in the ‘Swachata Abhiyan’ for their school and its neighbourhood. They separated out the biodegradable and non-biodegradable wastes and put them in separate bins. Their science teacher appreciated their work. She compared their work with the methods of ‘Sieving’ and ‘Winnowing’ about which she had taught them last week.
1. State the values displayed by the students of Class-VI.
Answer – The values displayed by the students are cleanliness, eco-friendly.
2. Give one example each of a situation in which ‘sieving’ and ‘winnowing’ can be used for bringing about the required separation.
Answer – Sieving can be used in households to separate the coarse particles from the wheat flour. Winnowing is used for separating the remaining husk from rice.
3. Have a discussion in the class, in which each group of students gives one example of ‘separation’, that can be compared with ‘some method of separation, studied by them.
Answer – Filtering tea from tea leaves by using a strainer is an example of the filtration method. Separating weeds from the spinach leaves before cooking is an example of handpicking.
Something To Do
1. Draw a neat and well-labelled diagram of filtration method. Also name the different varieties of filters available.
Answer – Different varieties of filters:
(1) Filter paper,
(2) Muslin cloth,
(3) Charcoal,
(4) Fine sand,
(5) Cotton wool.
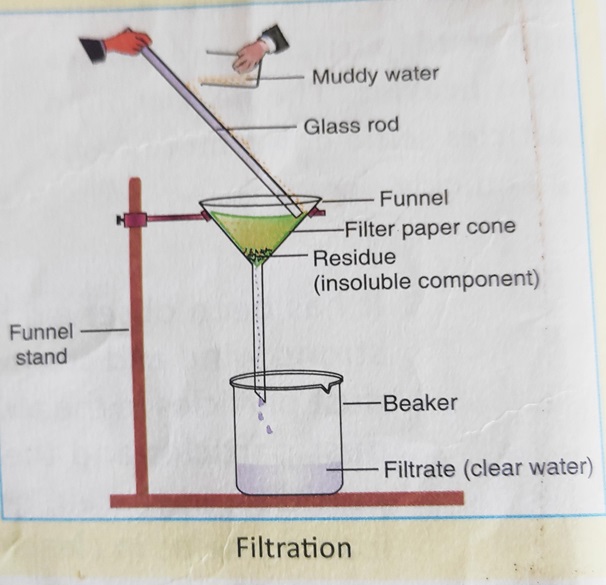
2. Fill a glass with impure water. Using your knowledge of methods of separation, suggest a method to purify it. Justify your suggestions.
Answer – Impure water can be purified by using a combination of sedimentation, decantation and filtration, if it is assumed that the water does not contain soluble impurities. First filtered liquid of all, the container is left undisturbed for residue some time so that some solid particles would settle down at the bottom. Then the liquid is poured in another container by the method of decantation. The liquid thus obtained is poured in a funnel which is lined with a filter paper. The filtrate thus obtained would be pure water.
3. Suggest ways to separate the components of the following mixtures.
(a) Camphor, sand and salt.
Answer – First of all, camphor should be separated from this mixture by using sublimation method. Then, the remaining mixture of sand and salt should be mixed with water. Salt shall dissolve in water and then sand can be separated by using filtration. Finally, salt can be separated from water by using evaporation method.
(b) Sawdust, common salt and iron nails.
Answer – First of all, iron nails should be separated by magnetic separation. After that, sawdust can be separated by using a sieve which is made of a very fine mesh.
(c) Ammonium chloride, common salt and chalk powder.
Answer – First of all, ammonium chloride should be separated from the mixture by using sublimation. Then, the remaining mixture of the chalk powder and salt should be mixed with water. Salt shall dissolve in water and then chalk powder can be separated by using filtration. Finally, salt can be separated from water by using evaporation method.
4. Visit the kitchen in your house and also your surroundings. Observe the different methods of separation that are being used by different people. Make a list of your observations and name the different methods used in different cases.
Answer –
| Substances | Method of separation |
| Pebbles from rice | Hand picking |
| Bran from flour | Sieving |
| Tea leaves from | tea Filtration |
| Cream from milk | Centrifugation |

