You Must Know
1. A flowering plant has two main parts the root system and the shoot system.
2. The root systems are of two types-tap root system and fibrous root system.
3. The root system gives support to the plant and absorbs water and minerals from the soil.
4. Some roots store food in them, or give additional support to the plant.
5. The shoot system, the part above the ground, bears stem, branches, leaves, flowers and fruits.
6. The stem transports water and minerals from roots to leaves, and provides support to the plant.
7. Some stems store food, manufacture food and also provide additional support.
8. Leaf is the green coloured, thin, broad and flat part of a plant.
9. Leaf prepares food through photosynthesis; it also helps in exchange of gases.
10. Leaf spine, leaf pitcher and leaf tendril, are some modifications in leaves which perform some special functions.
11. Flower is an organ of reproduction in plants; it grows into fruit and seed.
12. The main parts of a flower are sepal, petals, stamens and carpel.
13. The seed is a small hard structure, containing a baby plant; it stores food for its growth.
14. A fruit is defined as a mature, or ripened, ovary.
15. Fruit protects the seeds and helps in their dispersal.
Something To Know
A. Fill in the blanks.
1. Maize, wheat and rice are examples of fibrous roots.
2. Ginger and potato are two examples of modified stem.
3. The main function of the leaves is to prepare food for the plant.
4. Banyan is an example of prop roots.
5. Flower is the most attractive, and colourful, part of the plant.
6. The leaves of cacti are modified into spines.
7. The leaf blade is also known as lamina.
B. Write True or False for the following statements.
1. All plants possess the tap root system. False
2. The wheat and maize plants have a fibrous root system. True
3. Cactus plants photosynthesise through their stems. True
4. Leaves manufacture food for themselves. False
5. Flower is meant for the reproduction of the plant. True
6. The pistil is the female part of a flower. True
7. Stigma and ovary have no role in reproduction of plants. False
8. Seeds store food for the future plant. True
C. Tick (✔) the correct option.
1. The roots, that are consumed as food, are-
onion and sweet potato
carrot and onion
beet and turnip (✔)
potato and radish
Answer – beet and turnip(✔)
2. The plants manufacture food through the process of-
transpiration
photosynthesis (✔)
water conduction
respiration
Answer – photosynthesis(✔)
3. Leaves are attached to the stem at the-
nodes (✔)
internode
pedicel
stalk
Answer – nodes(✔)
4. The total number of whorls, in a flower, is/are—
one
two
three
four (✔)
Answer – four(✔)
5. The reproductive organ, of a plant, is the—
flower (✔)
seed
leaf
root
Answer – flower(✔)
6. The part of the flower, that provides protection to the bud, before it blooms, is the-
sepal (✔)
stamen
petals
pistil
Answer – sepal (✔)
D. Answer the following questions in brief.
1. Name the two main systems of a plant.
Answer – The two main systems of a plant are: The root system and the shoot system.
2. Name the different parts of the shoot system.
Answer – The different parts of the shoot system are: Stem, leaves, flowers, seeds and fruits.
3. Name different types of modified stems.
Answer – The different types of modified stems are:
Stems that stores food, eg. Potato
Stem that provides support eg. Stem tendrils.
Stem that manufactures food, eg. Cactus.
4. State the role of spines-the modified leaves.
Answer – Spines help to reduce the water loss in hot climates and also act as a defense organ for protection against grazing animals.
5. Name the different parts of a flower.
Answer – The different parts of a flower are: Sepals, Petals, Stamens, Pistil/Carpel, Pedicel.
6. Give the meaning of the term ‘pollination’.
Answer – The transfer of pollen grains, from anther to the stigma, is called pollination.
E. Answer the following questions.
1. State the differences between the two main systems of a plant.
Answer – The root system grows below the ground, while the shoot system grows above the ground.
Root system consists of roots while the shoot system consists of the stem, leaves, flowers, seeds and fruits. Root system grows towards gravity while the shoot system grows away from gravity.
2. Define root system. Give two functions of roots.
Answer – The root system grows below the ground.
The two functions of roots are:
(1) It fixes the plant in the soil.
(2) It absorbs water, and minerals, from the soil.
3. Define shoot system. Give two functions of the stem.
Answer – The Shoot system grows above the soil.
The two functions of stem are:
(1) It keeps the plant straight and upright.
(2) It transports food, prepared by the leaves, to all parts of the plant.
4. How is a tap root different from a fibrous root? Give one example of each type.
Answer – Single root that grows downwards into the soil, is called tap root. Example- Mustard. While, several roots that grow out at the same time from the base of the stem is called fibrous root. Example- Wheat.
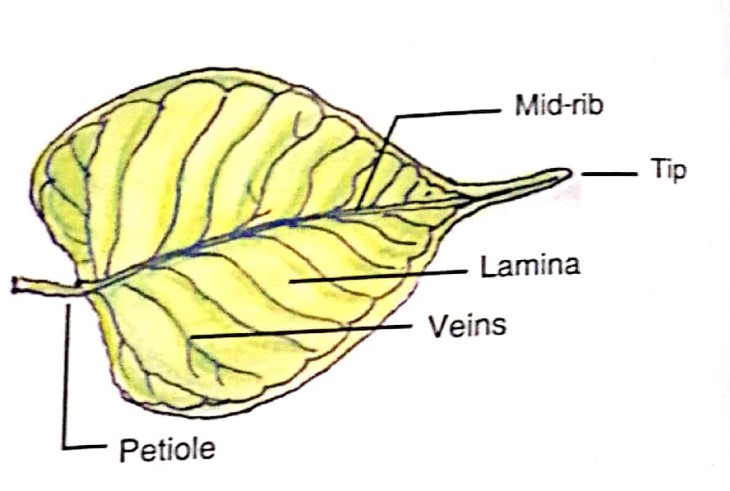
5. What is a leaf? Draw a diagram showing different parts of a leaf.
Answer – The leaf is the green coloured, thin, broad and flat part of a plant. It grows on the shoot at a node.
6. Name any two types of stem modifications, giving one example for each type.
Answer – The two types of stem modifications are:
(1) Stem that provides support. Example: Pea.
(2) Stem that stores food. Example: Potato.
7. Name the two parts of a stamen. State the functions of each of these two parts.
Answer – Answer: The two parts of a stamen are:
(1) Anther, which produces pollen grains that take part in reproduction.
(2) Filament, which provides support to the anther.
8. What are the functions of a fruit?
Answer – Functions of a fruit are:
(1) It helps in the dispersal of seeds.
(2) It protects the seed against injury and other Unfavorable climatic conditions.
(3) It stores food material, as in the case of tomato, apple and mange. fruits are the edible part of a plant.
Value Based Question
It was the occasion of the ‘Farewell day’ of Class-XII students. The principal wished them well and advised them to try becoming similar to the stem of the plants, for the elders and seniors in the family.
1. State the values that the principal wanted to convey to the students.
Answer – Virtue of providing strength and support to someone.
2. State any two of the functions that the stem performs during the life and growth of a plant.
Answer – Two functions of stem:
It provides support to various organs of the shoot system.
It supplies water and minerals to leaves.
3. Plan a ‘play’ in which different students play roles similar to the different functions of the stem/roots of a plant.
Answer – Teacher will do this activity.
Something To Do
1.Describe an experiment to show that water is transported by the root, through the stem, to all parts of the plant.
Answer – Take a twig and a bowl. Fill the bowl with coloured water and keep the twig in that; with the lower end in water. Keep it for about 2-3 days. After a few days, you will observe that the stem and the leaves have become coloured. We can conclude from this observation that water is transported through stem to all parts of the plant.
2. Draw a neat and well-labelled diagram of the structure of a flower.
Answer –

3. Take a potato. Examine it carefully. Look at the nodes and internodes present on it. In which category of the plant part would you place it?
Answer – Students will do this at their own.
4. Soak a few seeds of gram in water for a few days. Take them out and gently split them into two halves. Observe the position of the baby plant.
Answer – Students will do this at their own.
5. Visit your school garden. Get permission to collect a few flowers and observe them carefully. Count the number of sepals, petals, anthers and pistils. Split the anther and observe the pollen grains. Similarly, split open the ovary and see the ovules present in it.
Answer – Students will do this at their own.

